
About Aluminium
Aluminium is one of the most abundant metallic elements on Earth. It was previously difficult and expensive to extract, but the invention of the Hall-Héroult process in 1886 significantly reduced production costs, making it commercially available. Today, Aluminium is widely used in many industries, including aircraft, automobiles, construction, and packing, and is an essential material in our lives and industries.
-
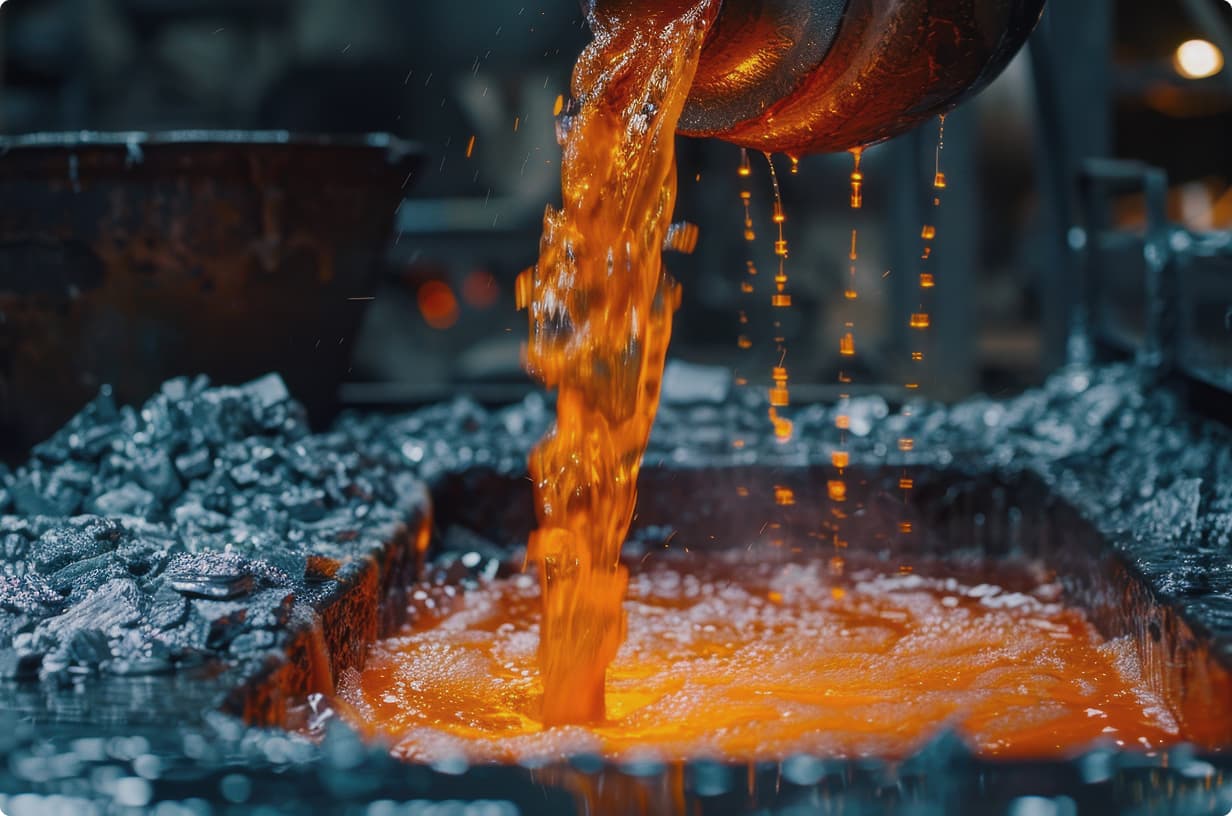

The aluminium production process begins with the mining of the main raw material, bauxite. Bauxite is refined into alumina (aluminium oxide) which is then electrolytically refined to obtain pure aluminium. This process is very energy intensive, so recycling of reclaimed aluminium is also important. Aluminium is a highly valued material due to its properties and versatility.
-

Aluminium alloys are alloys that have been made to improve performance by adding other metallic elements to the base aluminium. They have a very wide range of applications, and are used in countless products, including aircraft, automobiles, building materials, electronic devices, and kitchenware. In particular, weight reduction is a key point in the aircraft and automobile industries, and the demand for aluminium alloys is on the rise. There are also a wide variety of aluminium alloys, and the appropriate alloy is selected for each application.
-

When we think about the future of aluminium, it is very interesting to see how its many applications and ever-evolving technology will affect our lives. Future technological innovations will also lead to new applications that make the most of aluminium's properties. For example, the combination of nanotechnology could lead to the development of new materials that are incredibly light and strong. In conclusion, aluminium will play an increasingly important role in future industries and lives due to its diverse properties and sustainability. With technological advances, we can look forward to the future of aluminium opening up new possibilities.
Features of Aluminium
-

Lightweight
Aluminium is about one-third of iron or copper in weight, and is used in many industries. Its light weight also contributes to improving fuel efficiency in transportation.
-

High strength
Aluminium is attracting attention as an alternative to iron and steel because of its light weight and high strength. It is further strengthend by alloying and heat treatment.
-

High corrosion resistance
Aluminium forms an oxide film in the natural environment, providing excellent corrosion resistance even in harsh environments such as salt water and acid rain.
-

High ductility and workability
Aluminium can be processed in a variety of ways, including cutting, pressing, casting, and forging, and used to manufacture parts with complex shapes with high precision.
-
High thermal conductivity
Aluminium has excellent thermal conductivity among metals. This characteristic allows it to distribute heat efficiently and is suitable for applications that require uniform heat transfer.
-

High electrical conductivity
Aluminium has excellent electrical conductivity. Its electrical conductivity per unit weight is much higher than that of copper, and so it is increasingly used in areas where weight reduction is required.
-

Non-magnetic
Aluminium is a non-magnetic metal, which makes it extremely useful an environment free from the effects of electromagnetic waves.
-

Reflectivity
Aluminium is highly reflective and has the ability to effectively reflect light and heat, which provides a variety of benefits including improved energy efficiency, safety and aesthetics.
-
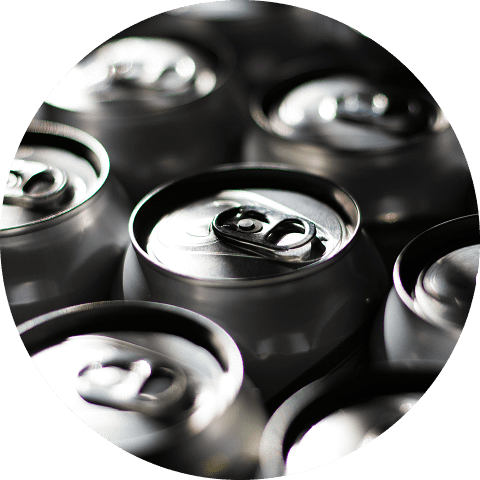

Recyclability
Aluminium is easy to recycle, its quality does not deteriorate, and recycling consumes approximately 95% less energy than producing new aluminium.
Aluminium around us
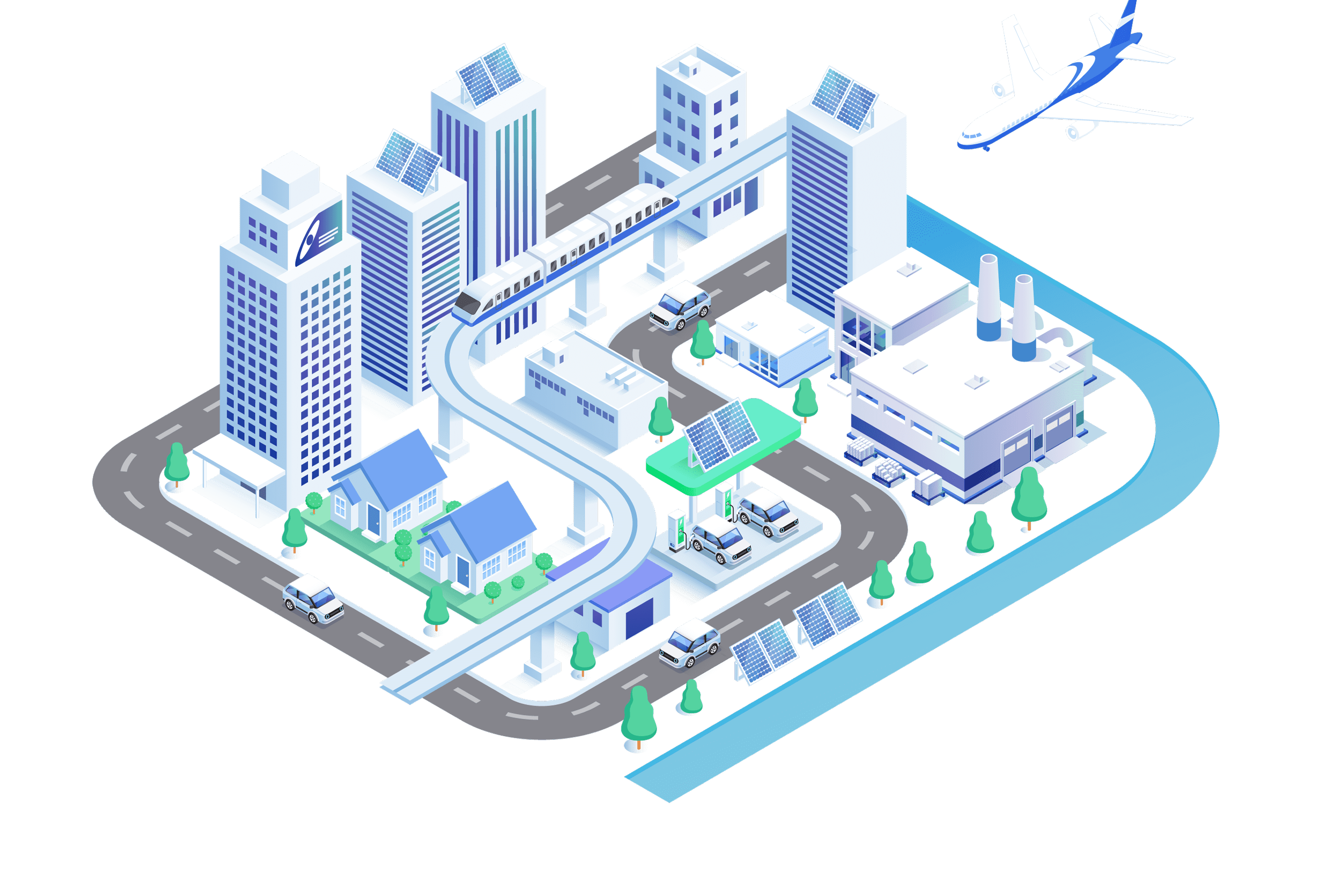

Factory
In addition to windows, it is used in various equipment and parts that require lightweight and corrosion resistance, such as piping, frames, control panels, workbenches, tools, transport equipment, and heat exchangers.

Buildings
Sash, curtain walls, handrails, exterior panels, roofing materials, interior materials, building fittings, etc. are widely used as lightweight, durable, and aesthetically pleasing building components.

Aircraft
Structures, wings, fuselage panels, frames, flooring materials, interior panels, and other components that require lightweight and high strength are widely used as primary structural materials.

Commercial facilities
Widely used as equipment with both design and durability, such as showcases, display shelves, signs, entrances, escalators, handrails, ceiling materials, and interior panels.

Automobiles
Engine parts, wheels, body panels, bumpers, radiators, suspension parts, interior parts, etc. are used in a variety of parts that take advantage of improved fuel efficiency through weight reduction and high processability.

Electronic devices
These components are widely used for their excellent thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity in enclosures, heat sinks, wiring materials, capacitors, circuit boards, shielding materials, heat dissipation components, and other applications.

Railways
These materials are widely used in railway vehicles and equipment as components that utilize energy efficiency and corrosion resistance achieved through weight reduction, such as vehicle bodies, flooring materials, seat frames, handrails, window frames, interior panels, and overhead wire support materials.

